Navigate SpaceX Texas Launch Facilities with Detailed Site Map
Detailed Overview of Starbase Facilities
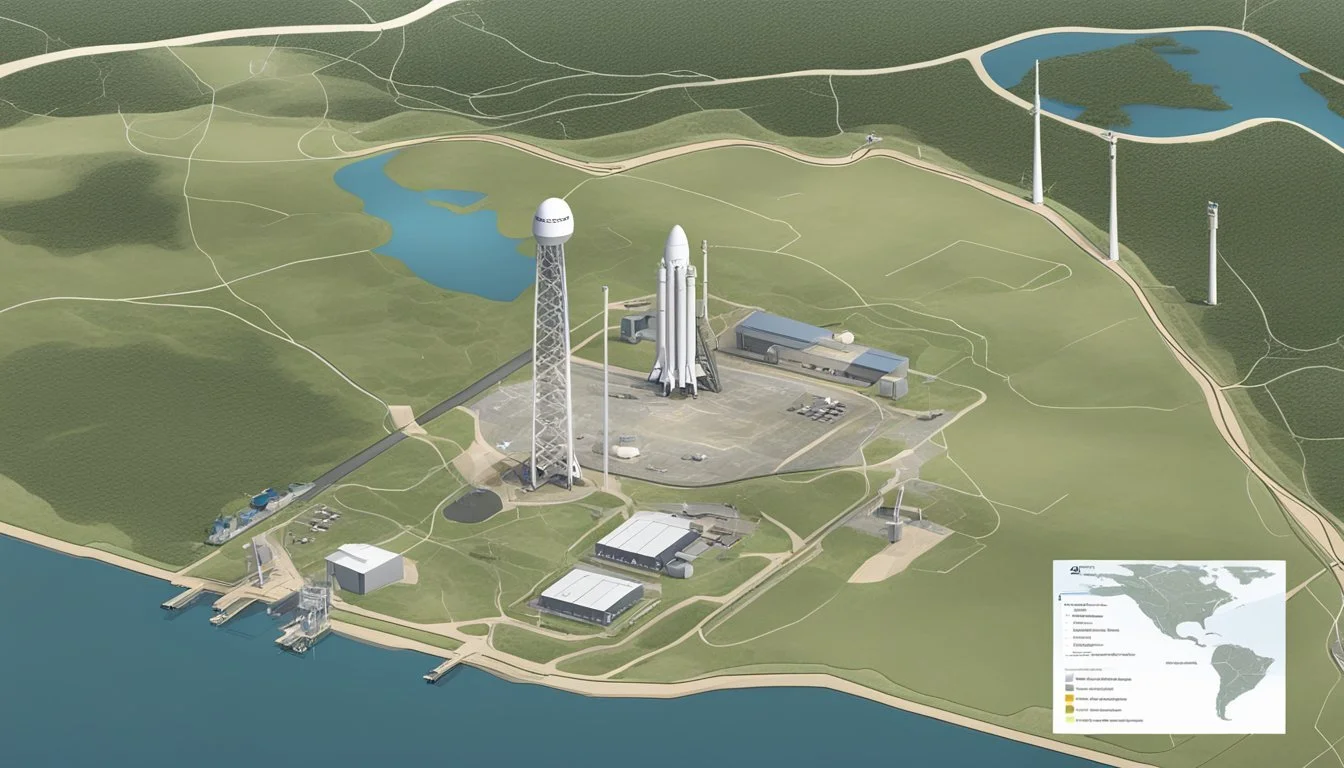
SpaceX's Starbase facility in Texas has become a focal point for space enthusiasts and rocket watchers. Located near Brownsville at Boca Chica, this sprawling complex serves as the primary testing and production site for SpaceX's ambitious Starship program. The launch site consists of three launch pads, including two suborbital pads and one orbital pad, spread across a landscape that has been transformed by SpaceX's presence.
Visitors to Starbase can witness the development of next-generation spacecraft firsthand. The facility stretches along a nearly three-kilometer road, with the launch site dominating the horizon. SpaceX has erected new signage at the launch site, marking its territory and signaling its long-term commitment to the area.
For those interested in tracking the progress at Starbase, aerial photography and regular flyovers provide up-to-date maps and imagery of the complex. These resources offer a bird's-eye view of the rapid changes occurring at the site, from new construction to the positioning of massive rocket prototypes awaiting their turn on the launch pad.
SpaceX and Starbase Overview
SpaceX's Starbase is a sprawling facility located in Boca Chica, Texas. It serves as the primary launch site and development center for the company's ambitious Starship program.
The complex encompasses several key areas:
Launch Site: Features orbital and suborbital launch pads
Production Facilities: Includes the Mega Bay and High Bay for vehicle assembly
Tank Farm: Stores propellants for launch operations
Rocket Garden: Displays retired or test vehicles
Starbase is where SpaceX builds and tests Starship prototypes. These vehicles use advanced Raptor engines, designed to power future missions to Mars and beyond.
Elon Musk, SpaceX's founder, envisions Starbase as a gateway to multiplanetary exploration. The site has seen rapid development since 2020, with frequent test flights and construction activities.
SpaceX continues to expand Starbase's capabilities. The company aims to conduct orbital Starship launches from this Texas location, marking significant milestones in space exploration.
Geography and Location
SpaceX's Starbase launch facility occupies a strategic coastal location in southernmost Texas. Its position offers both advantageous proximity to population centers and essential isolation for rocket testing and launches.
Proximity to Brownsville and Boca Chica
Starbase sits approximately 32 kilometers (20 miles) east of Brownsville, Texas. The facility's grounds stretch from the small community of Boca Chica Village to the shores of the Gulf of Mexico. This coastal position provides unobstructed launch paths over water, crucial for orbital missions.
The site borders Boca Chica State Park to the north and east. The Rio Grande marks the southern boundary, separating the launch complex from Mexico. This location balances accessibility with the necessary buffer zones for rocket operations.
Access via Highway 4
State Highway 4 serves as the sole road access to Starbase. The two-lane highway extends east from Brownsville, passing through Laguna Atascosa National Wildlife Refuge before reaching Boca Chica Village and the SpaceX facility.
The 32-kilometer stretch of Highway 4 from Brownsville to Starbase traverses mostly undeveloped land. This isolated corridor helps maintain security and safety during launch operations. SpaceX occasionally closes the highway during tests and launches, coordinating with local authorities to manage access.
Launch Facilities
SpaceX's Starbase in Texas houses multiple launch facilities designed for different purposes. These include an orbital launch pad for Starship, a suborbital testing area, and supporting infrastructure.
Orbital Launch Pad
The orbital launch pad is the centerpiece of Starbase's launch facilities. It features a massive launch mount designed to support the fully-stacked Starship and Super Heavy booster. The pad includes a 469-foot-tall integration tower, nicknamed "Mechazilla," equipped with robotic arms for vehicle stacking and launch operations.
Surrounding the pad are propellant storage tanks and ground support equipment. A flame diverter system helps protect the pad and equipment during liftoffs. The orbital pad's location near the Gulf of Mexico allows for over-water flight paths, enhancing safety for test launches.
Suborbital Pad B
Suborbital Pad B serves as a crucial testing ground for Starship prototypes. This smaller pad is used for static fire tests, short hops, and other development activities. It has its own propellant storage and fueling systems, separate from the orbital pad.
The suborbital pad played a key role in early Starship testing, hosting numerous prototype flights and engine tests. Its continued use allows SpaceX to conduct parallel testing and development activities without impacting orbital launch preparations.
Tank Farm and Water Deluge System
The tank farm stores cryogenic propellants needed for Starship and Super Heavy. It consists of multiple large tanks for liquid methane and liquid oxygen. The farm connects to both the orbital and suborbital pads via a network of pipes and valves.
A massive water deluge system protects the launch infrastructure from extreme heat and acoustic energy during liftoff. This system can pump thousands of gallons of water per second onto the pad and surrounding areas. It's a critical safety feature that also helps reduce potential damage to the facilities.
The tank farm area also includes a solar farm to help power Starbase operations, showcasing SpaceX's commitment to sustainable energy practices.
Launch Operations and Flight Tests
SpaceX's Starbase facility in Texas serves as the primary site for Starship and Super Heavy booster testing. The launch complex has undergone significant development to support orbital flight attempts.
Launch operations at Starbase involve extensive preparations and safety procedures. Before each test, the area is cleared and local residents are notified.
Flight tests have progressed from short "hops" to more ambitious suborbital and orbital attempts. Key milestones include:
First 150-meter hop in August 2020
10 km flight and landing attempt in December 2020
Orbital flight test in April 2023
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) oversees launch licensing and conducts environmental assessments. SpaceX must comply with FAA regulations for each test flight.
Starship's orbital test campaign aims to demonstrate full-stack capabilities. This involves launching the Super Heavy booster and Starship spacecraft to achieve orbital velocity.
SpaceX iterates rapidly between tests, incorporating data and improvements. The company's goal is to increase flight frequency and reliability over time.
Launch infrastructure at Starbase continues to evolve. New additions include the orbital launch mount, tank farm expansions, and catch arms for booster recovery attempts.
Historical and Future Missions
SpaceX's Texas launch site has played a crucial role in advancing space exploration. From groundbreaking test flights to ambitious plans for interplanetary travel, the facility continues to push the boundaries of rocketry and spaceflight.
Demo-2 and Commercial Launches
While not directly launched from Texas, the Demo-2 mission showcased SpaceX's capabilities, paving the way for future crewed launches. The successful flight in May 2020 marked the return of human spaceflight from U.S. soil after a nine-year hiatus.
SpaceX's Texas site focuses on Starship development. Though commercial launches currently occur at other SpaceX facilities, the Starbase aims to support future orbital flights.
The site has hosted numerous high-altitude tests of Starship prototypes, providing valuable data for the program's advancement.
Apollo Program Legacy
SpaceX's Texas launch site draws inspiration from NASA's Apollo program. While not directly involved in Apollo missions, the facility embodies the spirit of innovation that propelled humans to the Moon.
The Starship program aims to build upon Apollo's achievements, targeting sustainable lunar exploration and eventual Mars missions.
SpaceX's rapid prototyping and iterative design approach at the Texas site echo the fast-paced development seen during the Apollo era.
Gateway to Mars Initiative
SpaceX's Texas facility serves as the primary development and testing ground for the Starship program, central to the company's Mars ambitions.
The site has been dubbed "The Gateway to Mars" due to its critical role in advancing Starship technology.
Starship is designed to transport crew and cargo to Mars, with the Texas site playing a key role in perfecting launch and landing capabilities.
SpaceX aims to establish a sustainable presence on Mars, using Starship as the primary vehicle for both transit and surface operations.
The Texas launch site's location near the Gulf of Mexico allows for over-water testing, crucial for simulating planetary landings.
Comparison with Other SpaceX Sites
SpaceX operates multiple launch sites across the United States. The Texas facility differs from its Florida counterparts in several key aspects, including location, infrastructure, and operational focus.
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station
SpaceX's Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station plays a crucial role in the company's launch operations. This site primarily supports Falcon 9 missions, including commercial satellite deployments and cargo resupply to the International Space Station.
SLC-40 benefits from established infrastructure and long-standing partnerships with government agencies. The site's proximity to the Atlantic Ocean allows for easy downrange tracking and recovery of rocket boosters.
Unlike the Texas facility, SLC-40 is not designed for Starship operations. It focuses on proven Falcon 9 technology and commercial launches.
Kennedy Space Center Proximity
Launch Complex 39A (LC-39A) at Kennedy Space Center serves as SpaceX's premier launch site for crewed missions. Its location offers advantages for reaching various orbital inclinations.
LC-39A hosts both Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launches. The historic pad, once used for Apollo and Space Shuttle missions, has been modified to support SpaceX's operations.
The Launch Control Center at Kennedy Space Center coordinates activities for LC-39A. This facility provides advanced mission control capabilities and real-time communication with launch vehicles.
While the Texas site focuses on Starship development, LC-39A maintains a diverse launch manifest. It supports NASA's Commercial Crew Program and high-priority government payloads.
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations
SpaceX's Texas launch site is subject to extensive regulatory oversight and environmental scrutiny. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) plays a crucial role in this process.
The FAA conducted an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) for the SpaceX Texas launch site. This assessment evaluated potential environmental effects of the proposed facility and operations.
After the initial EIS, SpaceX modified its plans. The FAA performed several written re-evaluations to determine if additional environmental analysis was needed. These evaluations found that the original EIS remained valid.
The FAA requires SpaceX to implement over 75 actions to mitigate environmental impacts. These measures aim to protect the surrounding ecosystem, including nearby state parks and wildlife refuges.
Environmental groups have expressed concerns about the launch site's impact on local habitats. The area is home to numerous plant and animal species, some of which may be sensitive to disturbances.
SpaceX must comply with strict regulations to minimize ecological disruption. This includes managing noise levels, controlling debris, and limiting impacts on protected areas.
The company's launch plans are contingent on meeting these environmental requirements. Ongoing monitoring and assessments ensure compliance with established guidelines.
Amenities and Public Viewpoints
Visitors to SpaceX's Starbase in Texas have several options for viewing rocket launches and development activities. Key viewing locations include areas near Remedios Avenue and the historic Boca Chica Village.
Viewing Locations Near Remedios Ave
Remedios Avenue offers prime viewing spots for SpaceX activities. A popular location is "The Outpost," situated 3.7 miles from the launch site. This multi-level viewing area features a 30-foot tower, providing excellent vantage points for observing launches and tests.
Public roads near Remedios Avenue allow spectators to park and watch from a safe distance. Visitors should respect private property boundaries and stay on public land.
Boca Chica Village
Boca Chica Village, largely acquired by SpaceX, serves as housing for employees. While access is restricted, the village's proximity to launch and production sites makes it a notable area for SpaceX operations.
Some homes in Boca Chica Village have been upgraded with Tesla Solar Roofs and Powerwalls, showcasing SpaceX's integration of sustainable technologies.
Public areas near the village may offer glimpses of SpaceX activities, but visitors must adhere to local regulations and avoid trespassing on private property.
Maps and Accessibility
SpaceX's Starbase facility in Texas spans a large area, making maps essential for visitors and employees. The complex includes multiple sites spread across Boca Chica, near Brownsville.
Key locations on Starbase maps include the orbital launch pad, suborbital launch pads, and production facilities. The main launch site is situated approximately 3 kilometers (2 miles) from the nearest public viewing areas.
Accessibility to Starbase is limited due to security concerns and operational requirements. Public roads lead to designated viewing spots, allowing enthusiasts to observe from a safe distance.
Maps often highlight the village of Boca Chica, now largely owned by SpaceX and used for employee housing. These homes feature modern amenities like Tesla Solar Roofs and Powerwalls.
For those planning a visit, online maps and guides provide detailed information on permitted viewing locations. It's important to note that direct access to most Starbase facilities is restricted to authorized personnel only.
The nearest major city, Brownsville, serves as a base for many visitors. From there, clear signage and well-marked roads guide travelers to the public viewing areas near Starbase.
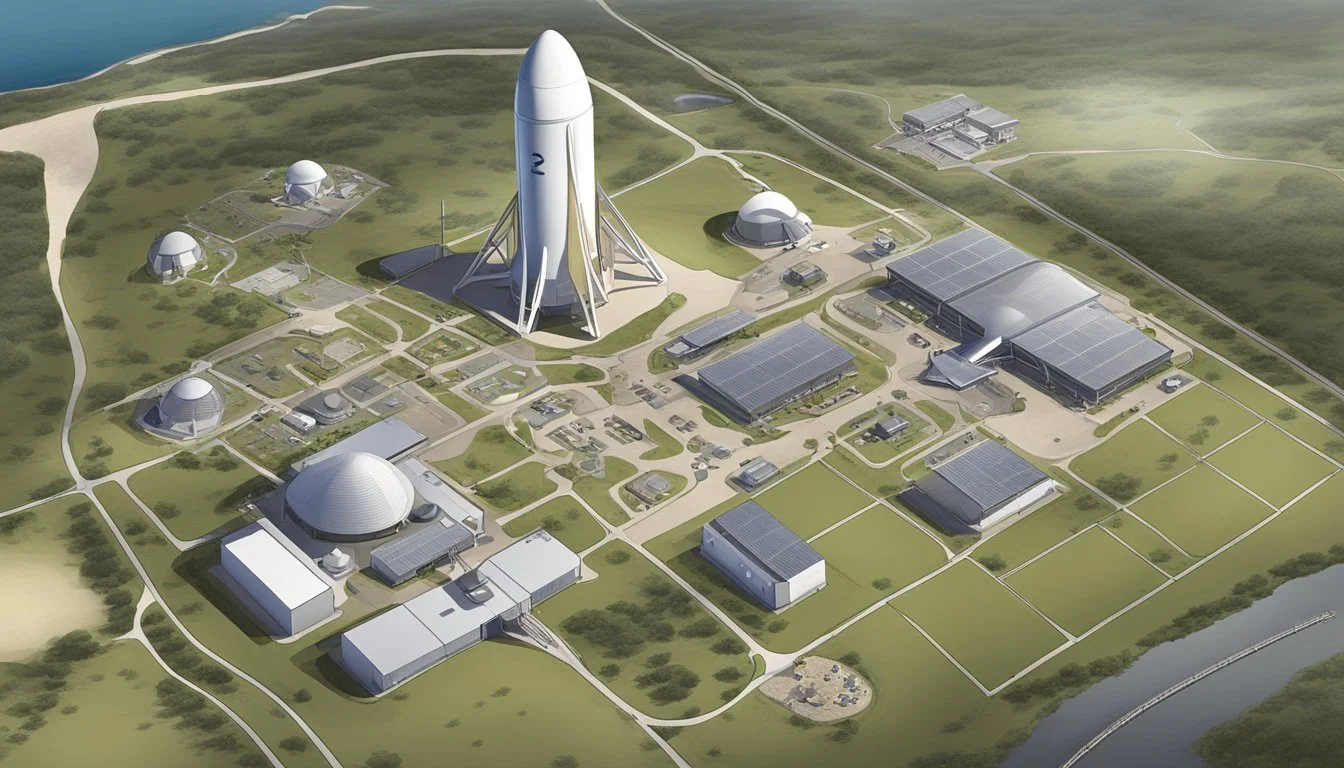
Supporting Infrastructure
SpaceX's Starbase in Texas relies on several key supporting facilities to enable rocket production and launch operations. These include large assembly buildings and a crucial staging area for equipment and infrastructure.
Mega Bays and Starfactory
The Mega Bays and Starfactory form the core of SpaceX's production capabilities at Starbase. These massive structures house the assembly lines for Starship and Super Heavy vehicles.
The Mega Bays consist of multiple high-bay facilities where technicians stack and integrate Starship components. These buildings feature tall ceilings to accommodate the full height of the spacecraft.
Adjacent to the Mega Bays, the Starfactory focuses on manufacturing individual sections and components. This facility uses advanced automation and robotics to streamline production processes.
A solar farm near these buildings helps power operations, aligning with SpaceX's sustainability goals.
Sanchez Site Development
The Sanchez site plays a critical role as a staging and assembly area for Starbase infrastructure. Located separate from the main launch complex, it provides ample space for equipment preparation.
Many key elements of Starbase were first assembled at the Sanchez site, including:
Orbital Launch Tower
Engine test stands
Propellant storage tanks
This location allows SpaceX to construct large structures away from active launch areas, minimizing disruptions to operations. Once complete, these components are transported to their final positions at the launch site.
The Sanchez site continues to serve as a flexible workspace for ongoing infrastructure projects and equipment staging.