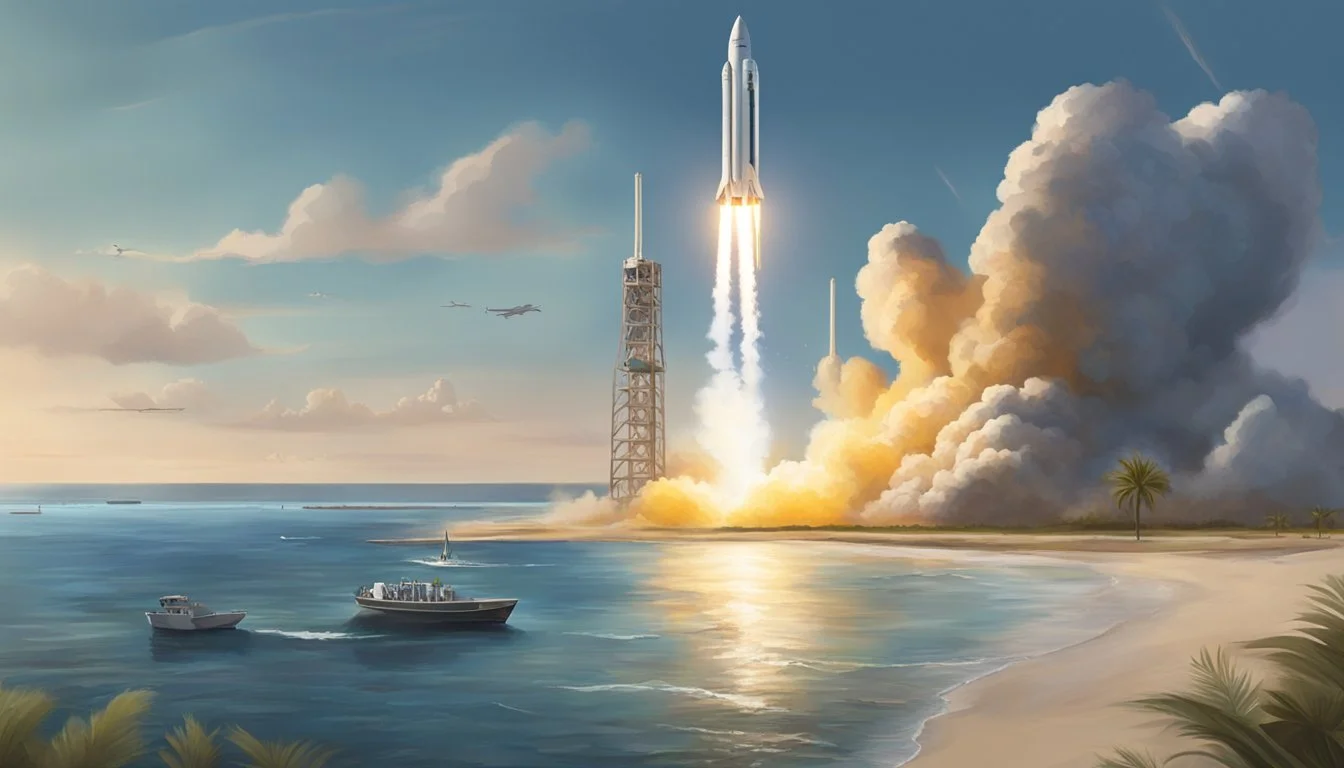
SpaceX Prepares Groundbreaking Starlink Mission from Boca Chica Site
SpaceX continues to push the boundaries of space exploration with its ambitious Starship program. The company's latest test flight, Flight 6, marks another milestone in the development of the world's largest and most powerful rocket system. Launched from the Starbase facility near Boca Chica, Texas, this mission represents the fourth Starship launch of 2024 and the sixth overall test flight of the fully integrated vehicle.
The nearly 400-foot-tall Starship rocket, consisting of the Super Heavy booster and the Starship spacecraft, aims to revolutionize space travel and enable missions to Mars. Each test flight brings SpaceX closer to its goal of making the vehicle fully reusable, a key factor in reducing the cost of space access. The recent Flight 5 mission saw a significant achievement when SpaceX successfully caught the Super Heavy booster using the launch tower's "chopsticks" mechanism, demonstrating progress in the rocket's recovery system.
As SpaceX continues to refine the Starship's capabilities, these test flights from Boca Chica serve as crucial stepping stones towards operational missions. The company's rapid iterative approach allows for quick improvements and modifications based on data gathered from each launch, steadily advancing the Starship program towards its ultimate goals of lunar landings and interplanetary travel.
SpaceX Overview
SpaceX revolutionized the aerospace industry with its innovative approach to space exploration and rocket technology. The company's ambitious goals and groundbreaking achievements have positioned it as a leader in commercial spaceflight.
History of SpaceX
SpaceX was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the goal of reducing space transportation costs and enabling the colonization of Mars. The company's early years were marked by challenges and setbacks.
In 2008, SpaceX achieved its first successful orbital launch with the Falcon 1 rocket. This milestone paved the way for larger contracts and more ambitious projects.
The development of the Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft followed, allowing SpaceX to secure contracts with NASA for cargo resupply missions to the International Space Station.
In 2015, SpaceX successfully landed a Falcon 9 first stage, marking a major breakthrough in reusable rocket technology. This innovation significantly reduced launch costs and increased the frequency of missions.
Elon Musk's Vision for SpaceX
Elon Musk's vision for SpaceX extends far beyond Earth's orbit. He aims to make humanity a multi-planetary species, with Mars as the primary target for colonization.
Musk believes that establishing a self-sustaining city on Mars is crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of human civilization. This ambitious goal drives SpaceX's development of the Starship spacecraft and Super Heavy booster.
The Starship project represents a key component of Musk's vision. It is designed to be a fully reusable launch system capable of carrying both crew and cargo to Mars, the Moon, and other destinations in the solar system.
SpaceX's rapid development of Starship prototypes at its Boca Chica facility in Texas demonstrates the company's commitment to Musk's vision. Regular test flights and iterative improvements showcase the progress toward achieving interplanetary travel.
Boca Chica Launch Site
SpaceX's Boca Chica launch site in Cameron County, Texas serves as a crucial facility for Starship development and testing. The coastal location provides strategic advantages for orbital launches and prototype flights.
Development of Boca Chica Facility
SpaceX began developing the Boca Chica site in 2014. The company selected this location for its proximity to the equator and over-water flight path. Initially envisioned as a commercial launch site, Boca Chica evolved into the primary testing ground for Starship.
The facility expanded rapidly, with the construction of production buildings, fuel storage tanks, and launch infrastructure. SpaceX renamed the site "Starbase" in 2021, reflecting its growing importance to the Starship program.
Environmental assessments were conducted to evaluate the impact on the surrounding area. These studies addressed concerns about wildlife habitats and local communities.
Importance of Boca Chica for SpaceX
Boca Chica plays a vital role in SpaceX's ambitious Starship development program. The site enables rapid prototyping and testing of Starship vehicles. Engineers can quickly iterate designs based on test flight results.
The coastal location allows for safe over-water test flights and eventual orbital launches. This reduces risks associated with flying over populated areas.
Boca Chica's facilities support the entire Starship development cycle. From manufacturing and assembly to static fire tests and launches, all crucial activities occur on-site. This integrated approach accelerates the pace of innovation.
The launch site's significance extends beyond testing. SpaceX envisions Boca Chica as a future spaceport for commercial Starship operations, including potential point-to-point Earth travel.
SpaceX Vehicles
SpaceX has developed multiple advanced spacecraft and rockets for orbital launches and space exploration. The company's vehicles include the next-generation Starship system and the reliable Falcon 9 and Dragon combination.
Starship and Super Heavy Booster
Starship is SpaceX's fully reusable spacecraft designed for missions to Earth orbit, the Moon, and Mars. It stands 50 meters tall and can carry over 100 metric tons to orbit. The Super Heavy booster propels Starship off the launch pad with 33 Raptor engines producing over 70 meganewtons of thrust.
Together, Starship and Super Heavy form the world's most powerful launch vehicle. The system is undergoing testing at SpaceX's Boca Chica facility in Texas. SpaceX aims to use Starship for satellite deployment, space tourism, and eventually interplanetary transport.
Falcon 9 and Dragon
Falcon 9 is SpaceX's workhorse orbital rocket. The two-stage vehicle stands 70 meters tall and can lift 22,800 kg to low Earth orbit. Its first stage is designed to land and be reused, significantly reducing launch costs.
Dragon is a reusable spacecraft that rides atop Falcon 9. It comes in two variants: Crew Dragon for transporting astronauts and Cargo Dragon for delivering supplies to the International Space Station. Dragon can carry up to 7 passengers or 6,000 kg of cargo.
SpaceX has launched Falcon 9 and Dragon over 100 times, demonstrating high reliability and revolutionizing the launch industry with rocket reusability.
Launch Process
SpaceX's Starship launches from Boca Chica involve meticulous preparation, precise execution during flight, and careful recovery operations. The process encompasses crucial stages from pre-launch checks to post-landing procedures.
Pre-Launch Preparations
The Launch Tower plays a vital role in pre-launch activities. Crews conduct thorough systems checks and load propellants into Starship and Super Heavy. Liquid methane and liquid oxygen are pumped into the vehicles' tanks through umbilical connections.
Weather conditions are closely monitored. Launch controllers verify all systems are go for liftoff. The launch pad is cleared of personnel, and nearby areas are evacuated for safety.
Final countdown procedures begin. Automated sequences take over, managing critical functions like pressurizing tanks and chilling engines.
Liftoff and Flight Procedures
At T-0, Raptor engines ignite. Starship lifts off from the launch mount, clearing the tower within seconds. The vehicle accelerates rapidly, following a predetermined flight path.
Stage separation occurs minutes into flight. Super Heavy booster detaches and begins its return. Starship's engines continue burning, propelling it to orbit or test altitude.
Flight controllers monitor telemetry data throughout ascent. They track the vehicle's trajectory, speed, and performance metrics.
Landing and Recovery Operations
As Starship completes its mission, it initiates descent procedures. The vehicle performs a "belly flop" maneuver, using its fins for aerodynamic control.
Near the ground, Starship executes a landing burn. Raptor engines reignite, slowing the craft for a vertical touchdown on the designated landing pad.
For ocean landings, recovery ships deploy to retrieve the vehicle after splashdown. Crews secure Starship and prepare it for transport back to Boca Chica.
Post-landing inspections begin immediately. Engineers assess the vehicle's condition and collect data for future improvements.
Key SpaceX Missions
SpaceX has undertaken numerous groundbreaking missions from its Boca Chica facility. These missions span commercial launches, NASA partnerships, and international collaborations, showcasing the company's versatility and technological prowess.
Commercial Payloads
SpaceX's Boca Chica site has become a hub for commercial satellite deployments. The company has launched multiple Starlink missions, expanding its global internet constellation. These missions typically deploy 60 satellites per launch, rapidly growing the network.
Falcon 9 rockets have also carried payloads for various private companies and organizations. These include communications satellites, Earth observation platforms, and experimental technology demonstrators.
The site's strategic location allows for efficient launches to equatorial and polar orbits, making it attractive for diverse commercial clients.
NASA Partnerships and Artemis Program
SpaceX's collaboration with NASA has led to significant missions from Boca Chica. The company has been integral to NASA's Commercial Crew Program, launching astronauts to the International Space Station.
The Artemis Program, NASA's initiative to return humans to the Moon, relies heavily on SpaceX's Starship. Boca Chica serves as the primary development and testing site for this next-generation spacecraft.
Starship prototypes have undergone multiple high-altitude tests at the facility, pushing the boundaries of reusable rocket technology. These tests are crucial for future lunar missions and potential Mars exploration.
International Collaborations and ISS Resupply
Boca Chica has played a vital role in SpaceX's international missions. The site supports launches for various global partners, including telecommunications companies and foreign space agencies.
SpaceX's Dragon capsule, launched from Boca Chica, regularly resupplies the International Space Station. These missions deliver essential cargo, scientific experiments, and crew supplies to the orbiting laboratory.
The facility has also supported deployments of satellites for international Earth observation programs and climate research initiatives. These missions contribute valuable data to global scientific efforts.
Innovation in Space Technology
SpaceX continues to push boundaries in space technology at its Boca Chica facility. The company's advancements in propulsion systems and spacecraft design are paving the way for future missions to the Moon and Mars.
Advancement in Raptor Engines
The Raptor engine represents a significant leap in rocket propulsion technology. These engines use liquid methane and liquid oxygen as propellants, offering improved efficiency and performance over traditional rocket engines. SpaceX has refined the Raptor design, increasing its thrust-to-weight ratio and reliability.
Recent tests at Boca Chica have demonstrated the Raptor's ability to withstand extended burn times, crucial for long-duration space flights. The engine's reusability factor has also improved, with each Raptor now capable of multiple firings without major refurbishment.
Engineers have implemented innovative cooling systems to manage the extreme temperatures generated during launch and reentry. These advancements contribute to the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of SpaceX's launch operations.
Spacecraft Design Innovations
SpaceX's Starship design incorporates cutting-edge features to withstand the rigors of space travel. The spacecraft's stainless steel construction provides strength and heat resistance, while also reducing manufacturing costs.
A key innovation is the heat shield composed of hexagonal tiles. These tiles protect Starship during atmospheric reentry, withstanding temperatures up to 1,477°C (2,690°F). The tiles are designed to be easily replaceable, streamlining maintenance procedures.
Starship's unique aerodynamic flaps allow for controlled descent and landing on both Earth and other celestial bodies. This design eliminates the need for traditional parachutes, enabling precision landings on diverse terrains.
The spacecraft's modular design facilitates rapid reconfiguration for various mission profiles, from satellite deployment to crewed missions to the Moon and Mars.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
SpaceX's Boca Chica launch site raises important environmental and safety considerations. The FAA requires extensive mitigation measures to address potential impacts on the surrounding ecosystem and ensure public safety during launches and landings.
Environmental Impact at Boca Chica
The SpaceX facility at Boca Chica is located near sensitive wildlife habitats. The FAA mandates over 75 actions to mitigate environmental effects. These include measures to protect endangered species and minimize disruption to local ecosystems.
Launch operations impact air quality through emissions and noise. Water resources are also affected, with large volumes used in the deluge system for launch pad cooling and sound suppression.
SpaceX must conduct ongoing environmental monitoring. This tracks changes to vegetation, wildlife populations, and water quality. The company is required to restore any damaged habitats and limit beach closures during launches.
Safety Protocols for Launch and Reentry
Strict safety measures govern Starship launches and landings at Boca Chica. SpaceX implements exclusion zones on land and at sea to keep the public away from potential hazards. These zones expand or contract based on mission profiles.
The company coordinates closely with local authorities on road closures and evacuations when necessary. Advanced tracking systems monitor vehicle trajectory during ascent and descent phases.
Automated flight termination systems can destroy the rocket if it veers off course. For reentry, SpaceX employs precision landing technology to guide Starship to designated landing pads. Firefighting teams and hazmat crews stand by to respond to any incidents.
SpaceX and Global Impact
SpaceX's operations at Boca Chica have far-reaching effects beyond the launch site itself. The company's activities generate economic benefits, inspire educational initiatives, and shape the future of spaceflight worldwide.
Economic Contributions
SpaceX's presence in Boca Chica has created thousands of jobs and boosted the local economy. The company employs over 3,400 people at the site, including engineers, technicians, and support staff.
This influx of workers has stimulated growth in surrounding areas. New businesses have opened to serve the SpaceX workforce and visitors drawn to rocket launches.
The economic impact extends beyond Texas. SpaceX contracts with suppliers across the United States and globally for specialized components and materials. This creates jobs and drives innovation in the aerospace supply chain.
Educational and Social Outreach
SpaceX actively engages with schools and universities to promote STEM education. The company offers internships and hosts educational events at Boca Chica, inspiring the next generation of engineers and scientists.
Rocket launches from the site have become popular attractions, drawing space enthusiasts from around the world. This tourism boost benefits local businesses and raises awareness of spaceflight.
SpaceX also partners with organizations to use its technology for humanitarian efforts. Starlink satellites provide internet access to remote areas in Africa, Asia, and other regions, improving education and healthcare services.
Influence on Global Spaceflight
SpaceX's achievements at Boca Chica have spurred competition in the global space industry. Countries like China and India have accelerated their own space programs in response.
The company's reusable rocket technology has reduced launch costs, making space more accessible. This has enabled new commercial and scientific missions, benefiting research and communication worldwide.
SpaceX's success has also influenced space policies. Governments in Europe, the Middle East, and Asia are reassessing their space strategies and investing in new capabilities to keep pace with private sector innovation.
Future Endeavors and Missions
SpaceX's ambitious plans for space exploration extend far beyond Earth orbit. The company aims to push the boundaries of human spaceflight and establish a permanent human presence on other celestial bodies.
Manned Missions to Mars
SpaceX is actively developing technology for crewed missions to Mars. The company has set an ambitious target of 2026 for its first Mars mission. This aligns with their recent tests of heat shield materials designed specifically for Mars entry. The Starship spacecraft, currently undergoing test flights, is being engineered to transport both crew and cargo to the Red Planet.
SpaceX plans to establish a fuel production facility on Mars using local resources. This in-situ resource utilization will enable return trips and sustained exploration. The company is also working on life support systems, radiation shielding, and habitat designs to ensure astronaut safety during long-duration Mars missions.
Long-Term Space Colonization Plans
SpaceX's vision extends to permanent human settlements beyond Earth. The Moon serves as a stepping stone for these efforts. The company is developing a Lunar Lander variant of Starship to support NASA's Artemis program and future lunar bases.
For Mars colonization, SpaceX aims to transport large numbers of settlers and supplies. Their plans include building pressurized habitats, greenhouses for food production, and infrastructure for water and oxygen generation. The company is researching technologies for Martian resource extraction and manufacturing to create self-sustaining colonies.
SpaceX's long-term goals involve establishing regular cargo and crew flights between Earth and Mars. This interplanetary transport system could eventually support a population of up to a million people on Mars, creating a backup for human civilization.
Public Engagement and Media
SpaceX's Boca Chica launch site has captured widespread public attention and media coverage. The company's innovative approach to spaceflight has influenced popular culture and sparked global interest in space exploration.
Media Coverage and Live Streaming Events
Major news networks like CNN regularly cover SpaceX launches from Boca Chica. These events attract millions of viewers worldwide through live TV broadcasts and online livestreams.
SpaceX provides its own high-quality livestream of launches, offering multiple camera angles and expert commentary. This direct access allows space enthusiasts to follow missions in real-time.
Social media platforms see a surge in activity during launches, with users sharing updates and reactions. Hashtags related to SpaceX and Starship often trend globally on these occasions.
News outlets frequently report on the progress of SpaceX's Starship development at Boca Chica. This ongoing coverage keeps the public informed about milestones and setbacks in the program.
SpaceX's Influence on Pop Culture
SpaceX has made space exploration more accessible to the general public. The company's sleek rocket designs and futuristic spacesuits have become iconic in popular media.
References to SpaceX and its founder Elon Musk appear in TV shows, movies, and video games. This exposure has helped spark renewed interest in space among younger generations.
SpaceX merchandise, including models of the Starship, has become popular among space enthusiasts. The company's branding and visual identity are now widely recognized.
The Boca Chica launch site itself has become a tourist attraction. Space fans often visit the area hoping to glimpse rocket tests or launches, boosting local tourism.
Challenges and Controversies
SpaceX's Boca Chica launch site has faced significant hurdles and public scrutiny. Legal issues, environmental concerns, and community opposition have complicated the company's operations in South Texas.
Legal and Regulatory Hurdles
SpaceX has encountered regulatory challenges at its Boca Chica facility. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) required environmental assessments before approving launches.
These reviews aimed to evaluate potential impacts on wildlife, air quality, and local ecosystems. SpaceX had to address concerns about noise pollution and debris scattering during test flights.
The company allegedly violated the Clean Water Act at the launch site. Reports suggest SpaceX sent pollution into nearby water bodies, prompting investigations by environmental agencies.
Public Perception and Criticism
Local residents and environmental groups have expressed concerns about SpaceX's presence in Boca Chica. Critics argue the launch site disrupts wildlife habitats and restricts public beach access.
The Surfrider Foundation sued the FAA over the environmental impact of SpaceX operations. They cited inadequate assessment of harm to species and beach closures.
Some community members worry about safety risks from rocket tests and launches. Explosions and debris scattering have heightened these fears.
SpaceX faces accusations of using preserved lands as a buffer for its operations. This has sparked debate about the balance between space exploration and environmental preservation.