Musk's Mars Madness: Billionaire's Secret Alien Pact Promises Immortality on Red Planet!
Elon Musk's ambitious plan to colonize Mars has captivated the world's imagination. Through his company SpaceX, Musk aims to establish a self-sustaining city on the Red Planet within the next few decades. SpaceX intends to begin launching uncrewed Starship rockets to Mars as early as 2026, marking a significant milestone in this interplanetary endeavor.
The Starship spacecraft and Super Heavy rocket form the cornerstone of SpaceX's Mars colonization program. These fully reusable vehicles are designed to transport both humans and cargo to the Martian surface. SpaceX has conducted several test flights of Starship prototypes, with plans to attempt a full orbital launch and recovery of both stages in the near future.
Musk envisions a thriving Martian settlement of one million inhabitants by the 2060s. This audacious goal faces numerous technical, logistical, and environmental challenges. Yet SpaceX continues to push forward, developing technologies for in-situ resource utilization and sustainable habitation on Mars. As the company refines its spacecraft and launch systems, the dream of humans becoming a multi-planetary species inches closer to reality.
Elon Musk's Vision for Mars
Elon Musk envisions a future where humans become a multiplanetary species, with Mars as the first destination beyond Earth. His ambitious plans draw inspiration from science fiction while aiming to turn imagination into reality.
Multiplanetary Species Ambitions
Musk's primary goal is to establish a self-sustaining city on Mars. He believes this is crucial for humanity's long-term survival and expansion. SpaceX, Musk's aerospace company, is developing the Starship spacecraft to transport people and cargo to the Red Planet.
The planned Mars city would start small, gradually expanding to accommodate up to a million inhabitants. Musk emphasizes the need for a diverse skill set among early settlers to build essential infrastructure.
He proposes using local Martian resources to produce fuel, oxygen, and building materials. This approach, known as in-situ resource utilization, is key to reducing reliance on Earth and making the settlement sustainable.
Influence of Science Fiction on Mars Exploration
Science fiction has played a significant role in shaping Musk's vision for Mars colonization. He often cites Isaac Asimov's Foundation series as a major influence, particularly its concept of preserving human knowledge across vast distances.
The idea of terraforming Mars to make it more Earth-like also stems from science fiction. While Musk acknowledges this as a long-term possibility, his immediate focus is on creating habitable structures on the planet's surface.
Musk's plans echo themes from classic Mars novels, such as Ray Bradbury's "The Martian Chronicles." These stories have helped fuel public interest in Mars exploration and colonization.
SpaceX's Roadmap to Mars
SpaceX has ambitious plans to reach Mars through a series of technological advancements and mission milestones. The company's strategy involves leveraging powerful rockets and spacecraft designed for interplanetary travel.
Falcon Heavy and Its Role
Falcon Heavy serves as a crucial stepping stone in SpaceX's Mars ambitions. This powerful rocket can lift over 63 metric tons to low Earth orbit, making it ideal for launching heavy payloads.
Falcon Heavy has already demonstrated its capabilities through successful test flights and commercial missions. Its ability to launch large satellites and spacecraft paves the way for future Mars-bound cargo.
The rocket's reusable boosters significantly reduce launch costs, a key factor in making Mars missions more economically feasible.
Development of Starship
Starship represents the cornerstone of SpaceX's Mars colonization efforts. This fully reusable spacecraft is designed to transport both crew and cargo to the Red Planet.
SpaceX has conducted several test flights of Starship prototypes, gradually improving its design and performance. The company aims to achieve orbital flights as a crucial milestone in Starship's development.
Starship's heat shield and life support systems are being refined to withstand the harsh Martian environment. SpaceX plans to use Starship for initial uncrewed Mars missions before attempting human landings.
Importance of the Super Heavy Booster
The Super Heavy booster is essential for launching Starship beyond Earth's orbit. This massive first stage provides the necessary thrust to escape Earth's gravity with a fully-loaded Starship.
Super Heavy utilizes multiple Raptor engines, offering unprecedented power and efficiency. SpaceX is working on perfecting the booster's landing and rapid reusability to enable frequent Mars missions.
The integration of Starship and Super Heavy creates the world's most powerful launch system, capable of delivering substantial payloads to Mars. This combined stack is crucial for establishing a sustainable presence on the Red Planet.
The Architecture of Interplanetary Transport
SpaceX's Interplanetary Transport System aims to enable human colonization of Mars. The architecture relies on advanced propulsion, orbital refueling, and reusable components to make interplanetary travel feasible and cost-effective.
Raptor Engines Advancement
The Raptor engine is a crucial component of SpaceX's Mars architecture. These methane-fueled engines provide high thrust and efficiency for both the booster and spacecraft. Raptor engines use a full-flow staged combustion cycle, allowing for improved performance compared to traditional rocket engines.
SpaceX has continually refined the Raptor design, increasing its thrust capabilities and reliability. The latest iterations can produce over 230 tons of thrust at sea level. Multiple Raptor engines work in tandem to power the massive rockets required for interplanetary missions.
Refueling in Earth Orbit
Orbital refueling is a key aspect of the Interplanetary Transport System. After launching from Earth, the spacecraft docks with a fuel depot in low Earth orbit. This allows the vehicle to be fully refueled before embarking on its journey to Mars.
The process involves multiple tanker flights to fill the depot. Each tanker uses the same reusable booster as the main spacecraft, maximizing efficiency. Orbital refueling enables the transport ship to carry a much larger payload to Mars than would be possible with a single Earth launch.
Sustainability and Reusability of Rockets
Reusability is central to SpaceX's Mars architecture. Both the first stage booster and the spacecraft itself are designed to be fully reusable. The booster returns to Earth after launch, landing vertically for refurbishment and reuse.
On Mars, the spacecraft is refueled using locally-produced propellant for the return journey. This approach drastically reduces mission costs compared to expendable rockets. SpaceX aims to achieve rapid reusability, with minimal refurbishment between flights.
The system's sustainability extends to Mars operations. In-situ resource utilization will produce methane fuel and oxygen from the Martian atmosphere, enabling return flights and expanding human presence on the red planet.
Mars Settlement Strategies
Elon Musk's vision for Mars colonization centers on establishing a permanent human presence on the Red Planet. The plan involves developing self-sustaining cities and overcoming significant challenges of the Martian environment.
Establishing a Self-Sustaining City
SpaceX aims to create a self-sufficient Martian city capable of supporting a large population. The strategy involves sending multiple Starship vehicles loaded with supplies, equipment, and settlers.
Initial efforts would focus on building habitats, power generation systems, and life support infrastructure. Settlers would utilize in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) to produce water, oxygen, and fuel from Martian resources.
Greenhouses would be crucial for food production, using Martian soil enriched with organic matter. Recycling systems would manage waste and reclaim valuable resources.
The city's growth would rely on regular supply missions from Earth until achieving self-sufficiency in critical areas like food, water, and energy production.
Challenges of Human Settlement on Mars
Settling Mars poses numerous obstacles. The harsh Martian environment, with its thin atmosphere and extreme temperatures, necessitates advanced life support systems.
Radiation exposure is a significant concern, requiring shielded habitats and protective gear for surface activities. The low gravity on Mars may lead to health issues for long-term settlers, including bone and muscle loss.
Psychological challenges of isolation and confinement in a hostile environment must be addressed. Developing reliable communication systems with Earth is crucial for settler well-being and mission success.
CO2 management is essential, both for creating breathable air and as a resource for producing fuel and other materials. Minimizing environmental impact on Mars while establishing settlements remains a key consideration.
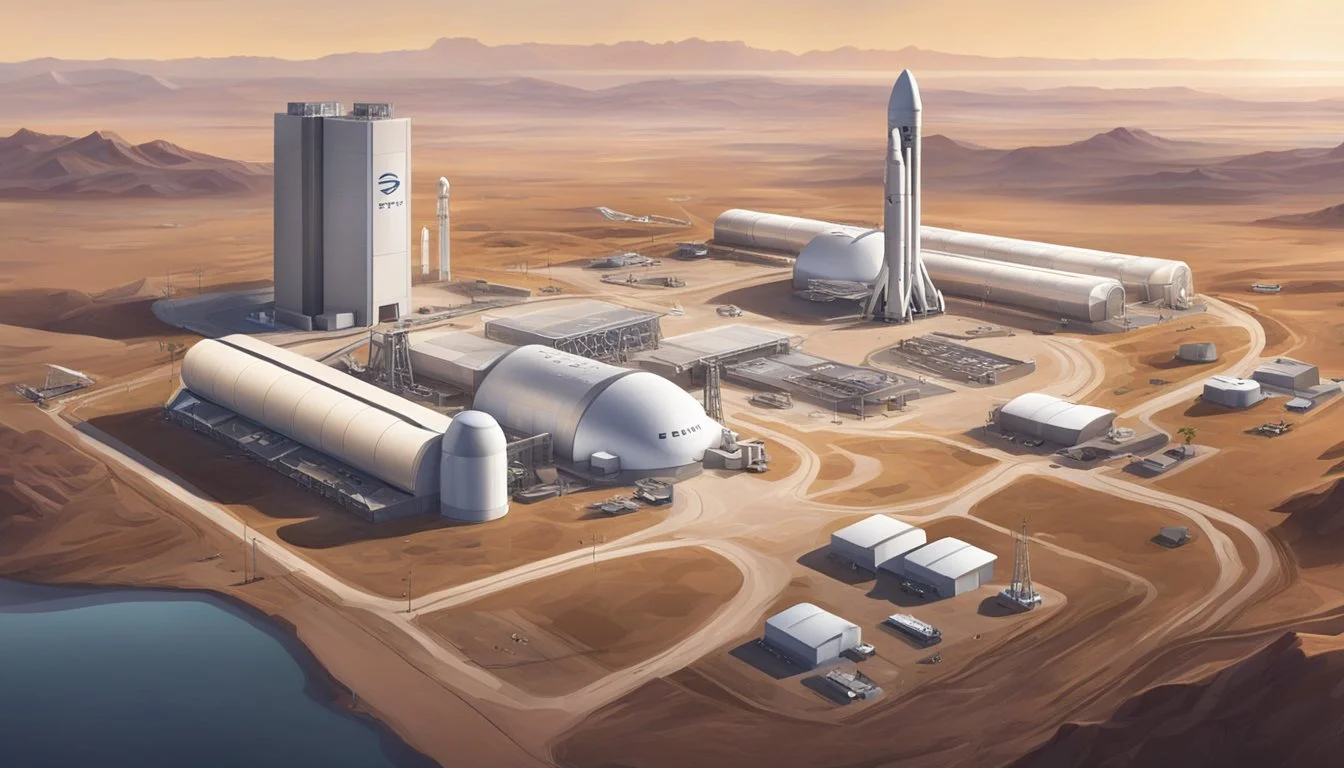
SpaceX Launch Facilities and Infrastructure
SpaceX has developed advanced launch facilities to support its ambitious space exploration goals. These sites enable rocket launches, spacecraft testing, and development of technologies for future Mars missions.
Starbase Operations
Starbase, located in Boca Chica, Texas, serves as SpaceX's primary launch and development site for Starship rockets. The facility includes a massive launch and catch tower, standing approximately 480 feet tall. This tower supports vehicle integration, launches, and booster recovery.
SpaceX chose Boca Chica in 2014 for its strategic location and favorable launch conditions. The site has evolved from a testing ground into a large-scale production facility. Starbase houses manufacturing, assembly, and testing operations for Starship vehicles.
The facility enables rapid prototyping and iterative development of SpaceX's next-generation spacecraft. Starbase's coastal location provides access to over-water flight corridors for testing and orbital launches.
Partnership with Federal Aviation Administration
SpaceX works closely with the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to ensure safe and compliant operations at its launch facilities. The FAA oversees licensing and regulation of commercial space activities in the United States.
This partnership involves rigorous safety reviews, environmental assessments, and launch authorizations. SpaceX must obtain FAA approval for each launch campaign, including flight plans and safety measures.
The FAA conducts ongoing monitoring of SpaceX operations to verify compliance with regulations. This oversight extends to public safety, airspace management, and environmental protection around launch sites.
SpaceX and the FAA collaborate to develop new frameworks for emerging technologies like Starship. This cooperation aims to balance innovation with safety in commercial spaceflight.
Milestones and Future Missions
SpaceX has made significant progress in its Mars ambitions through test missions and ambitious timelines. The company aims to send the first crewed mission to Mars in the coming years, marking a pivotal moment in space exploration.
Historical Test Missions
SpaceX's journey to Mars began with crucial test flights of its Starship spacecraft. In 2019, the company launched Starhopper, a prototype for testing Raptor engines and vertical takeoff and landing capabilities.
Subsequent Starship prototypes, SN8 through SN15, underwent high-altitude tests. SN15 achieved the first successful landing in May 2021, a major milestone for the program.
In April 2023, SpaceX attempted the first full-stack launch of Starship and Super Heavy booster. While the mission ended in an explosion, it provided valuable data for future attempts.
Upcoming Mars Mission Timelines
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk announced plans to start launching uncrewed Starships to Mars in 2026. These initial missions will focus on establishing basic infrastructure and testing landing capabilities.
If successful, the first crewed flights to Mars could follow as early as 2028. This ambitious timeline aligns with favorable launch windows, which occur approximately every 26 months when Earth and Mars align.
SpaceX aims to send multiple Starships during each launch window. These missions will transport cargo, supplies, and eventually astronauts to establish a sustainable presence on the Red Planet.
The company continues to refine Starship's heat shield and life support systems to ensure crew safety during the long journey and harsh Martian environment.
Biographical Overview
Elon Musk's Mars ambitions are deeply intertwined with key figures and ventures that have shaped his path. These connections highlight the collaborative nature of space exploration and technological innovation.
Gwynne Shotwell's Impact on SpaceX
Gwynne Shotwell joined SpaceX in 2002 as Vice President of Business Development. Her leadership has been crucial in transforming SpaceX from a startup to a major player in the aerospace industry.
Shotwell's expertise in sales and business strategy complemented Musk's visionary approach. She played a pivotal role in securing NASA contracts, which provided essential funding for SpaceX's development.
Under Shotwell's guidance, SpaceX achieved numerous milestones, including the first private spacecraft to dock with the International Space Station. Her contributions have been instrumental in advancing Musk's Mars colonization goals.
Wernher von Braun's Legacy
Wernher von Braun's work in rocketry significantly influenced modern space exploration, including Musk's Mars plans. Von Braun's designs for the Saturn V rocket enabled the Apollo missions to the Moon.
His vision of Mars colonization, outlined in his 1952 book "The Mars Project," anticipated many challenges that SpaceX now faces. Von Braun's technical expertise and advocacy for space exploration laid groundwork for future missions.
Musk has cited von Braun's work as inspirational, particularly his emphasis on reusable rockets. This concept is central to SpaceX's strategy for making Mars missions economically viable.
Elon Musk's Parallel Ventures: Tesla and Its Synergy
While pursuing Mars colonization through SpaceX, Musk has simultaneously led Tesla, creating synergies between the two companies. Tesla's advancements in electric vehicle technology and energy storage systems have applications for Mars missions.
The company's solar energy solutions could be adapted for use on Mars, addressing power generation challenges. Tesla's work on autonomous driving systems may inform the development of robotic explorers for the Martian surface.
Musk's leadership of both companies has fostered a culture of innovation and cross-pollination of ideas. This approach has accelerated progress in sustainable energy and space technologies, both crucial for Mars colonization efforts.