Tesla Austin Environmental Crisis: Pollution and Compliance Issues Exposed!
Tesla's Austin Gigafactory, a cornerstone of the company's electric vehicle production, has come under scrutiny for its environmental practices. Recent reports highlight concerns about pollution and regulatory compliance at the Texas facility.
The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality has conducted multiple investigations into Tesla's Austin plant, uncovering issues related to waste management and air pollution. These findings raise questions about the company's commitment to environmental stewardship and its impact on the local ecosystem.
Whistleblowers and internal documents suggest that Tesla may have overlooked environmental hazards at the Austin production site. This situation mirrors problems reported at the company's Fremont, California factory, indicating a potential pattern of environmental challenges across Tesla's manufacturing operations.
Background of Tesla Austin Gigafactory
Tesla's Austin Gigafactory represents a major expansion for the electric vehicle manufacturer. The facility plays a crucial role in Tesla's production capabilities and economic impact on the region.
Tesla's Expansion to Austin
Tesla announced plans for its Austin Gigafactory in July 2020. The company selected a 2,100-acre site in Travis County, Texas for the $1.1 billion manufacturing facility. Construction began quickly, with the factory becoming operational in less than two years.
The Austin location offers several strategic advantages for Tesla. Texas provides business-friendly policies and a central location within the United States. The area also boasts a skilled workforce and strong technology sector.
Importance of the Austin Factory
The Austin Gigafactory significantly boosts Tesla's production capacity. It manufactures the Model Y SUV and serves as the primary facility for the Cybertruck. The factory aims to produce up to 500,000 vehicles annually at full capacity.
Beyond vehicle production, the Gigafactory houses battery cell manufacturing and Tesla's engineering headquarters. This vertically integrated approach allows for greater control over the supply chain and production processes.
The facility has created thousands of jobs in the Austin area. It has also attracted suppliers and other businesses to the region, amplifying its economic impact. The Gigafactory showcases Tesla's commitment to large-scale manufacturing in the United States.
Environmental Oversight and Regulations
Tesla's Austin Gigafactory has become the focal point of changes in environmental oversight. The company has leveraged new state legislation to alter its regulatory landscape, impacting how environmental protections are applied and enforced at the facility.
State Law and Environmental Protections
In 2024, Tesla utilized a new Texas state law to exempt its Austin Gigafactory from the city's environmental regulations. This move allowed the company to remove 2,100 acres of its property from Austin's jurisdiction. The law, effective since September 1, enables Tesla to operate with fewer local restrictions.
The shift in oversight raises questions about environmental safeguards. While Tesla gains more autonomy, concerns emerge about potential impacts on local ecosystems and resources. The Colorado River, adjacent to the factory site, may face altered protection measures under this new arrangement.
Role of TCEQ and EPA
With Austin's reduced oversight, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) takes on a more prominent role in regulating Tesla's operations. The TCEQ is responsible for enforcing state environmental guidelines at the Gigafactory.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) maintains federal-level supervision. This agency ensures Tesla complies with national standards for air and water quality. The interplay between state and federal regulators becomes crucial in maintaining environmental protections.
Tesla must now navigate a complex regulatory landscape. The company balances state-granted freedoms with ongoing federal requirements. This situation highlights the evolving nature of environmental governance in Texas's industrial sector.
Impact on Local Water Resources
Tesla's Gigafactory in Austin has raised concerns about its effects on local water resources. The facility's operations have implications for wastewater management and the quality of the nearby Colorado River.
Wastewater Management Challenges
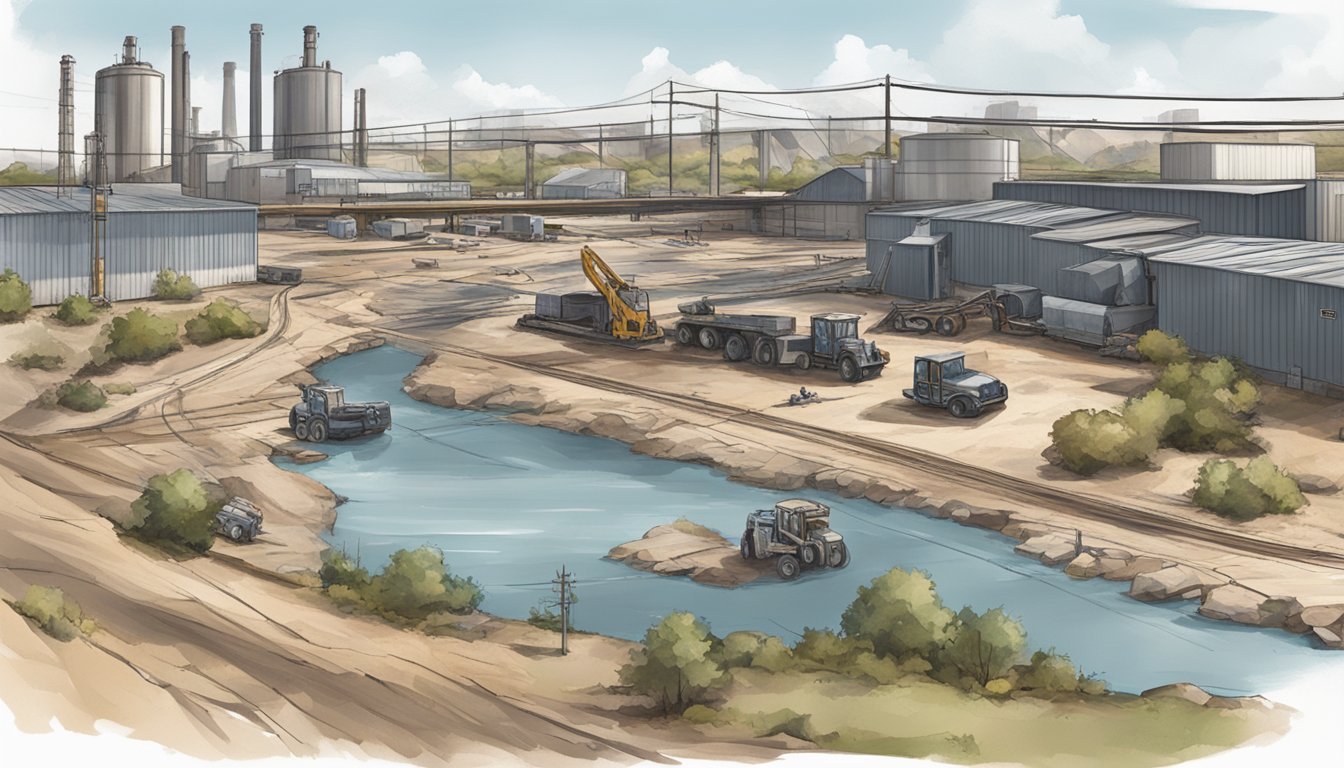
Tesla's Austin Gigafactory has faced issues with wastewater disposal. The company reportedly discharged water from a pond into Austin's sewer system without proper authorization from local regulators. This unauthorized disposal highlights the challenges in managing industrial wastewater at such a large-scale facility.
Tesla has received warnings from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality regarding its environmental practices. The company's attempts to remove waste have allegedly impacted nearly a mile of the local Colorado River tributary.
These incidents underscore the need for improved wastewater management protocols at the Gigafactory to minimize environmental risks.
Quality of the Colorado River
The Colorado River, a vital water source for the Austin area, faces potential impacts from Tesla's operations. Reports suggest that pollutants from the Gigafactory have been dumped into local waters, raising concerns about water quality.
Environmental regulators have pursued action against Tesla for these alleged violations. The company's activities may affect the river's ecosystem and the broader water supply for the region.
Tesla's use of a new state law to shed Austin's environmental oversight further complicates efforts to protect the Colorado River's water quality. This regulatory change could have long-term implications for monitoring and controlling industrial impacts on local water resources.
Air Quality and Emission Standards
Tesla's Austin Gigafactory has faced scrutiny over its environmental practices, particularly regarding air quality and emissions. The facility's operations have raised concerns about potential violations and pollution control measures.
Monitoring Air Violations
The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) has been actively monitoring Tesla's Austin factory for air quality violations. Reports indicate that the facility has received warnings related to its environmental activities. A malfunctioning casting furnace at the plant released toxins into the air, prompting regulatory action.
The TCEQ has pursued investigations into these incidents, focusing on the factory's compliance with state and local air quality regulations. Environmental groups and local residents have expressed concerns about the potential impact on the surrounding area's air quality.
Implementation of Air Pollution Controls
Tesla has been required to implement air pollution control measures at its Austin Gigafactory. These controls aim to reduce emissions and ensure compliance with environmental standards. The company has invested in advanced filtration systems and emission reduction technologies.
However, the effectiveness of these measures has been questioned. Reports suggest that Tesla may have bypassed some of Austin's air quality policies due to a new Texas law. This legislation potentially allows the factory to operate under different environmental rules than those enforced by the city.
Tesla's commitment to improving air quality around its facility remains under scrutiny. The company faces ongoing challenges in balancing rapid production growth with environmental responsibility.
Tesla's Environmental Commitment
Tesla aims to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy. The company's environmental initiatives and responses to concerns demonstrate its approach to balancing industrial growth with ecological responsibility.
Sustainability Initiatives
Tesla incorporates renewable energy into its manufacturing processes. The Gigafactory in Austin utilizes solar panels and energy storage systems to reduce reliance on the grid.
The company focuses on minimizing waste through recycling programs and efficient material use. Tesla's battery recycling efforts aim to recover valuable materials and reduce environmental impact.
Electric vehicle production inherently supports sustainability by promoting zero-emission transportation. Tesla's cars, solar products, and energy storage solutions contribute to reducing global carbon emissions.
Response to Environmental Concerns
Reports of environmental violations at Tesla's Austin factory have prompted scrutiny. The company faced allegations of improper wastewater disposal and air quality issues.
Tesla addressed these concerns by working with local authorities to ensure compliance. The company invested in improved water treatment systems and air quality control measures.
Public backlash led Tesla to increase transparency about its environmental practices. The company now provides more detailed reports on its sustainability efforts and impact.
Tesla continues to navigate challenges between rapid expansion and environmental regulations. The company's use of a new Texas law to bypass some local environmental rules has sparked debate about corporate responsibility and regulatory oversight.
Industrial Processes and Risks
Tesla's Austin Gigafactory involves complex manufacturing processes that carry potential environmental hazards. Proper handling of materials and prevention of spills are critical to minimizing risks.
Hazardous Materials Handling
Tesla's production lines utilize various hazardous substances in battery and vehicle manufacturing. These include toxic chemicals, solvents, and heavy metals. Proper storage, use, and disposal of these materials is essential.
Workers must follow strict safety protocols when handling hazardous materials. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment and using specialized containment systems.
The factory has designated areas for storing chemicals safely away from high-traffic zones. Automated systems help track inventory and usage of hazardous substances to prevent overuse or improper handling.
Regular employee training on hazardous material procedures is mandatory. This covers proper labeling, storage, and emergency response in case of accidental exposure or spills.
Preventing Chemical Spills
Spill prevention is a top priority to protect workers and the environment. The factory utilizes containment systems like berms and sealed flooring in chemical storage and use areas.
Leak detection systems provide early warnings of potential spills. Automated shutoffs can quickly stop chemical flows if leaks are detected.
Spill response equipment and teams are stationed throughout the facility. This includes absorbent materials, neutralizing agents, and personal protective gear.
The factory has detailed spill response plans for different chemical types. Regular drills ensure workers can execute these plans quickly and effectively if needed.
Proper maintenance of equipment that uses or transports chemicals is critical. This includes regular inspections of pipes, valves, and storage tanks to identify potential failure points before leaks occur.
Responses to Environmental Incidents
Tesla faced scrutiny over environmental issues at its Austin factory. Regulatory investigations and whistleblower claims prompted responses from the company and government agencies.
Investigation of Whistleblower Claims
The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) conducted 15 investigations into Tesla's Austin factory operations. These probes were triggered by whistleblower reports and focused on potential environmental violations.
A key issue involved a 30-foot furnace with a faulty door that remained open for months. Former employees reported this malfunction allowed pollutants to escape and increased temperatures in the work area.
The TCEQ examined claims of toxic pollutant discharge into local water sources. Regulatory documents and interviews with ex-employees highlighted concerns about waste management practices at the facility.
Tesla's Public Disclosures
Tesla's response to environmental incidents at its Austin plant has been limited in public forums. The company has not widely addressed specific allegations or investigation findings.
In corporate communications, Tesla continues to emphasize its commitment to sustainable manufacturing. However, detailed explanations of remediation efforts or policy changes in response to TCEQ investigations remain scarce.
The contrast between Tesla's public image as an environmentally conscious company and the reported incidents has drawn attention. This discrepancy has led to increased calls for transparency regarding the company's environmental practices and incident responses.
Local Community and Environmental Impact
Tesla's Austin Gigafactory has generated both opportunities and concerns for the surrounding area. The facility's development has raised questions about water management, land use, and regulatory oversight in the region.
Flooding and Land Management
The Tesla Gigafactory is located in an area prone to flooding. This has led to worries about potential environmental impacts on nearby water sources. The factory's construction involved significant land clearing and reshaping, altering the local landscape.
Tesla has implemented water management systems to mitigate flooding risks. These include retention ponds and drainage infrastructure. However, some environmental groups express concern about the effectiveness of these measures during major storm events.
The Wall Street Journal reported allegations of toxic pollutant discharge from the factory into local waters. Tesla disputes these claims, stating they comply with all relevant environmental regulations.
Extra-Territorial Jurisdiction Concerns
The Austin Gigafactory is situated on unincorporated land within Austin's extraterritorial jurisdiction (ETJ). This unique location has created regulatory complexities. Tesla has utilized a Texas state law to exempt the factory from some of Austin's environmental regulations.
This move has sparked debate about oversight and environmental protection. Local officials argue it limits their ability to enforce stricter standards. Supporters contend it allows for more efficient development and job creation.
The factory's location in the ETJ also impacts infrastructure development and public services. It raises questions about responsibility for road maintenance, utilities, and emergency response in the area.
Supplementary Business Ventures and Impact
Tesla's presence in Austin extends beyond vehicle manufacturing, encompassing partnerships and events that shape the local ecosystem. These initiatives demonstrate Tesla's multifaceted approach to innovation and community engagement.
Relationship with SpaceX and Boring Company
Tesla's Austin operations benefit from synergies with Elon Musk's other ventures. SpaceX collaborates on advanced materials and manufacturing techniques, enhancing Tesla's production capabilities. The Boring Company explores potential underground transportation solutions for the Gigafactory campus.
These partnerships foster a culture of cross-pollination, attracting top talent to the Austin area. Engineers and researchers move fluidly between projects, accelerating technological advancements.
The proximity of these companies creates a hub for cutting-edge technology development in central Texas. This ecosystem attracts suppliers, startups, and research institutions, further solidifying Austin's position as a tech powerhouse.
Impact of the Cyber Rodeo Event
The Cyber Rodeo, held at Tesla's Austin Gigafactory, served as a grand opening celebration and showcase of the company's vision. The event attracted thousands of attendees, including employees, customers, and industry partners.
Highlights included:
Unveiling of new vehicle prototypes
Demonstrations of advanced manufacturing processes
Interactive exhibits showcasing Tesla's energy products
The Cyber Rodeo generated significant media attention and economic activity for the Austin area. Local businesses reported increased sales during the event period.
Long-term impacts include:
Elevated interest in electric vehicles among Texas consumers
Strengthened relationships with local suppliers and partners
Increased tourism and business travel to the Austin region
The event solidified Tesla's commitment to the Austin community and its role as a major economic driver in the area.